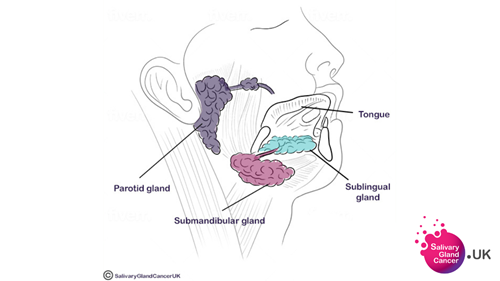
Major Salivary Glands - Parotid, Sublingual and Submandibular
The salivary glands in our bodies our divided into the major and minor salivary glands.
The major glands are much larger in size and secrete into a salivary duct, producing much more saliva than the minor salivary glands in the head and neck area. This saliva keeps the mouth and other parts of the digestive tract moist. Saliva moistens food and help you to swallow, break down and ultimately digest food. The glands can malfunction, become blocked and swollen.
In the head and neck area until recently there were three pairs of major salivary glands identified:
- The parotid gland, located behind the jaw in front of the ear
- The sublingual gland, located under the tongue
- The submandibular gland, located under the jaw
In 2021 the Tubarial Salivary Glands were found located in the nasopharynx - behind the nose.
There are also many other (600-1000) tiny minor salivary glands throughout the mouth, throat, inside the cheeks and in the lips. This includes the hard palate, the floor of the mouth and between the muscle fibres of the tongue. They are 1-2mm in size.
Salivary gland cancer can occur in the salivary glands but they can also happen in other secretory glands around the body, including the trachea, the vulva and the breast.
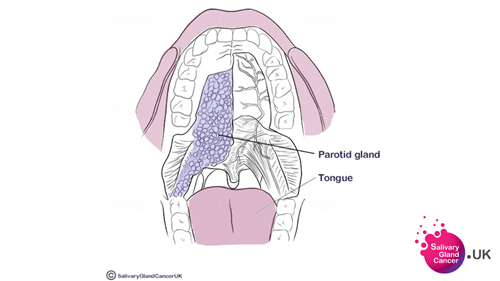
The Parotid Gland
The largest salivary gland - the parotid gland - produces a watery saliva that helps with digestion and mouth lubrication. This watery saliva drains into the mouth around the upper cheeks via the Stenson duct, keeping the mouth lubricated for speech and swallowing, as well as helping with food digestion.
The gland is located around the side of the jaw, in front of and around the ear as well as in the roof of the mouth. About 85% of salivary gland tumours occur in the parotid gland. Most are benign.
The Submandibular Gland
The submandibular glands (previously known as the submaxillary glands) are located just under and deep in the jaw towards the back of the mouth. The submandibular duct (called Warhitin's duct) carries the saliva from the gland and enters the floor of the mouth under the front of the tongue.
The submandibular glands produce 70% of the saliva in the mouth and although they are much smaller than the parotid gland. They can become blocked and form salivary duct stones if you are persistently dehydrated. Only about 10% of tumours start in the submandibular glands.
Sublingual Gland
The sublingual gland is the smallest of the major salivary glands and is located under the tongue. Literally sub = under/lingua = tongue. The sublingual glands supply saliva to the floor of the mouth.
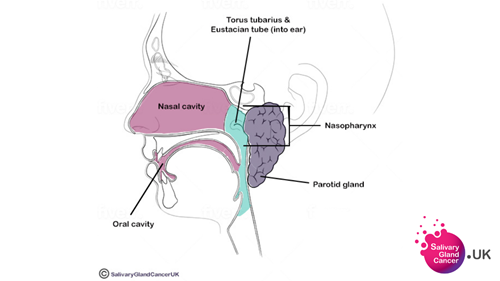
Tubarial Glands - Major or Minor Salivary Gland?
Discovered in 2020-2021! New salivary gland organs called ‘Tubarial glands’ were discovered in the nasopharynx by researchers in the Netherlands. The nasopharynx is the upper part of the throat behind the nose. An opening on each side of the nasopharynx leads into the ear (eustachian tubes). It is 2-3cm wide by 3-4cm long.
The nasopharynx contains adenoidal fluid to fight infection and also provides a major drainage path for lymphatic fluids, draining into the throat, nose or ears. Torus Tubarius - or eustachian cushion - is a mucous ridge in the nasopharynx behind the auditory (eustachian) tube. The new mucous gland tissue with draining ducts were found over the Torus Tuberous hence the name Tubarial glands.